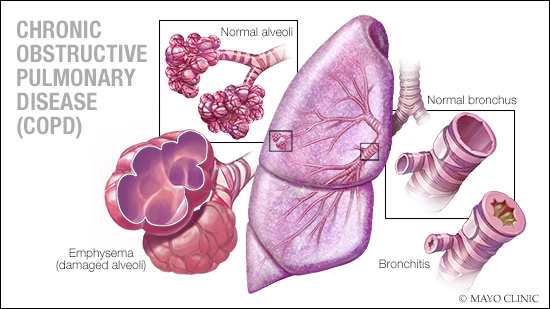
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, is a leading cause of disability and death in the U.S., according to the American Lung Association.
COPD is a chronic inflammatory lung disease most often caused by long-term smoking, especially cigarettes. Another cause of COPD is breathing in toxic fumes or gases. People with COPD are at increased risk of developing respiratory infections, heart disease, lung cancer, pulmonary hypertension and depression.
Symptoms of COPD often don't appear until significant lung damage has occurred, and they usually worsen over time, particularly if cigarette smoke exposure continues.
Signs and symptoms of COPD can include:
- Chest tightness
- Chronic cough that may produce clear, white, yellow or green mucus
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Lack of energy
- Unintended weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling in the ankles, feet or legs
- Wheezing
Most cases of COPD in the U.S. are directly related to long-term cigarette smoking. Stopping smoking can prevent COPD from worsening and reducing your ability to breathe. Treatment for COPD can include medications, such as inhalers; oxygen; pulmonary rehabilitation; in-home noninvasive ventilation therapy; managing flare-ups, also called exacerbations; endobronchial valves; and surgery.
For more information about strategies that can help people with COPD feel better and slow the damage to their lungs please visit the Mayo Clinic News Network.
 Connect
Connect
 Connect
Connect